Stainless Steel Crowns (SSCs)
Stainless steel crowns are used to restore back teeth that are too badly decayed to hold white fillings. When tooth decay on back teeth has been left untreated, teeth may have extensive damage to the enamel, dentin and sometimes the nerve (pulp). In such cases, tooth-colored fillings are not a viable option, and stainless steel crowns necessary. These prefabricated sliver-colored crowns are fit; then cemented onto the primary (baby) teeth to prevent further damage until these teeth are naturally lost.
Tooth Colored Fillings (Composite Resin)
Tooth colored fillings are used to restore front or back teeth or where cosmetic appearance is important. Composites are used to repair fractured teeth and/or areas of decay. The shade of the composite restorative material is matched as closely as possible to the color of the natural teeth.
X-Rays (Radiographs)
In general, children need X-rays more often than adults. Their mouths grow and change rapidly. X-rays can often show weaknesses in the tooth structure (such as demineralization) that may not be visible with the naked eye. The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry recommends X-ray examinations every six months for children with a high risk of tooth decay. Children with a low risk of tooth decay require X-rays less frequently. We use digital radiography which uses approximately 1/4 the radiation of the traditional dental x-rays.
Dental Cleaning (Prophylaxis)
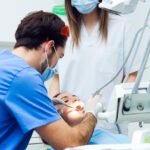
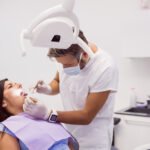
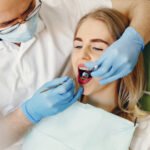
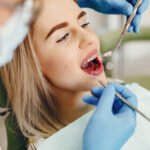
During a dental visit, the dental assistant or hygienist will first review your child’s medical history with you.Then your child’s mouth will be examined for overall oral health. Next, your child’s teeth will be thoroughly cleaned to remove plaque and calculus (hard tarter deposits), which can cause cavities and gum disease. After the cleaning, fluoride will be applied to the teeth to help protect and strengthen the weak areas against decay. For a healthy child, the American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry recommends a visit to the pediatric dentist at least every six months to evaluate your child’s oral health and development. However, if your child has special needs or is more predisposed to dental caries, the dentist may recommend more frequent visits to more closely manage your child’s oral health.
Fluoride
Cavities form when there is a weakening in the mineral composition of the enamel of your teeth. Fluoride promotes the remineralization of these decalcified spots, therefore helping to prevent cavities. Low level of fluoride is found naturally in some bodies of water. Municipal water supplies are often fluoridated to a specific standard level. Fluoride can also be found in many household products such as toothpaste, mouth rinses, and even some bottled water.
Pit and Fissure Sealant
Pit and fissure sealants, or simply fissure sealants are a dental treatment intended to prevent tooth decay. Teeth have recesses on their biting surfaces; the back teeth have fissures (grooves) and some front teeth have cingulum pits. It is these pits and fissures which are most vulnerable to tooth decay, partly because food sticks in them and they are hard to clean areas. Dental sealants are materials placed in these pits and fissures to fill them in, creating a smooth surface that is easy to clean. Dental sealants are mainly used in children who are at higher risk of tooth decay, and typically they are placed as soon as the adult molar teeth come through.